What is CBD?
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds that are naturally found in the cannabis plant, sometimes called phytocannbinoids. They are one of the primary components responsible for the various effects of cannabis in the human body. Cannabinoids interact with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex regulatory system involved in maintaining physiological balance and homeostasis.
Endocannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds within the human body that are similar in structure to cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. "Endo" stands for "endogenous," which means they originate within the body. These compounds, along with their receptors and enzymes, make up the endocannabinoid system.
The two most well-known cannabinoids found in cannabis are:
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive cannabinoid found in all species of cannabis. This compound works primarily by mimicking the effects of anandamide, an endocannabinoid which assists in a myriad of bodily functions.
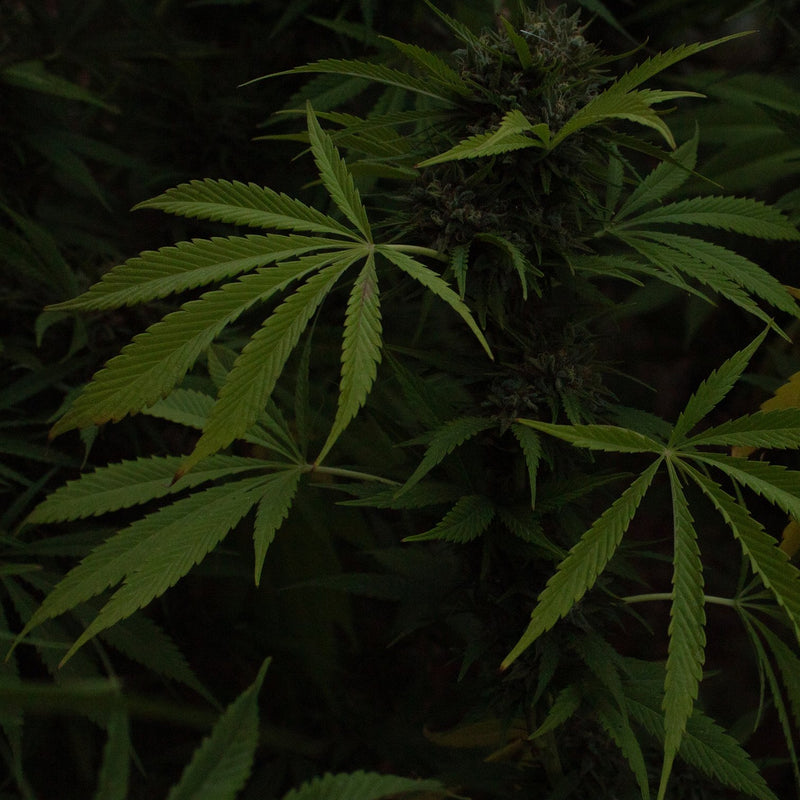
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the second most-prominent cannabinoid found in the plant and is generally considered to be non-psychoactive. CBD can be derived from all cannabis species but is primarily derived from hemp or Cannabis sativa.
In addition to THC and CBD, there are over 100 other cannabinoids present in cannabis, each with its own unique properties. Some of these lesser-known cannabinoids include cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and cannabichromene (CBC). Research into these compounds and their effects on the body is ongoing.
Endocannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds within the human body that are similar in structure to cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. "Endo" stands for "endogenous," which means they originate within the body. These compounds, along with their receptors and enzymes, make up the endocannabinoid system.
The two most well-known cannabinoids found in cannabis are:
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive cannabinoid found in all species of cannabis. This compound works primarily by mimicking the effects of anandamide, an endocannabinoid which assists in a myriad of bodily functions.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the second most-prominent cannabinoid found in the plant and is generally considered to be non-psychoactive. CBD can be derived from all cannabis species but is primarily derived from hemp or Cannabis sativa.
In addition to THC and CBD, there are over 100 other cannabinoids present in cannabis, each with its own unique properties. Some of these lesser-known cannabinoids include cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and cannabichromene (CBC). Research into these compounds and their effects on the body is ongoing.








LEARN MORE ABOUT CBD
SHOP CBD